Iftikhar Alam
Author
Reviewed by Cannabis Experts
Published on: April 13, 2021 | Updated on: July 27, 2024
The popularity of vaping cannabis has skyrocketed. This contemporary smoking substitute has gained popularity as a possibly healthier alternative. Vaping is gentler on the lungs because there is no combustion or harmful chemicals. Furthermore, lower temperatures assist to retain each strain’s unique flavor.
The key to unleashing whatever benefits a strain has to give is temperature management. If you want to get the advantages of a CBD-rich strain, for example, you must heat it to the compound’s boiling point of 356 degrees Fahrenheit. Similarly, the calming terpene linalool isn’t released until the temperature reaches 388 degrees Fahrenheit. The strength of a strain can also be determined by its temperature; greater temperatures tend to accentuate effects, whilst lower temperatures provide a more mild, mellow sensation.
Why temperature matters for vaping
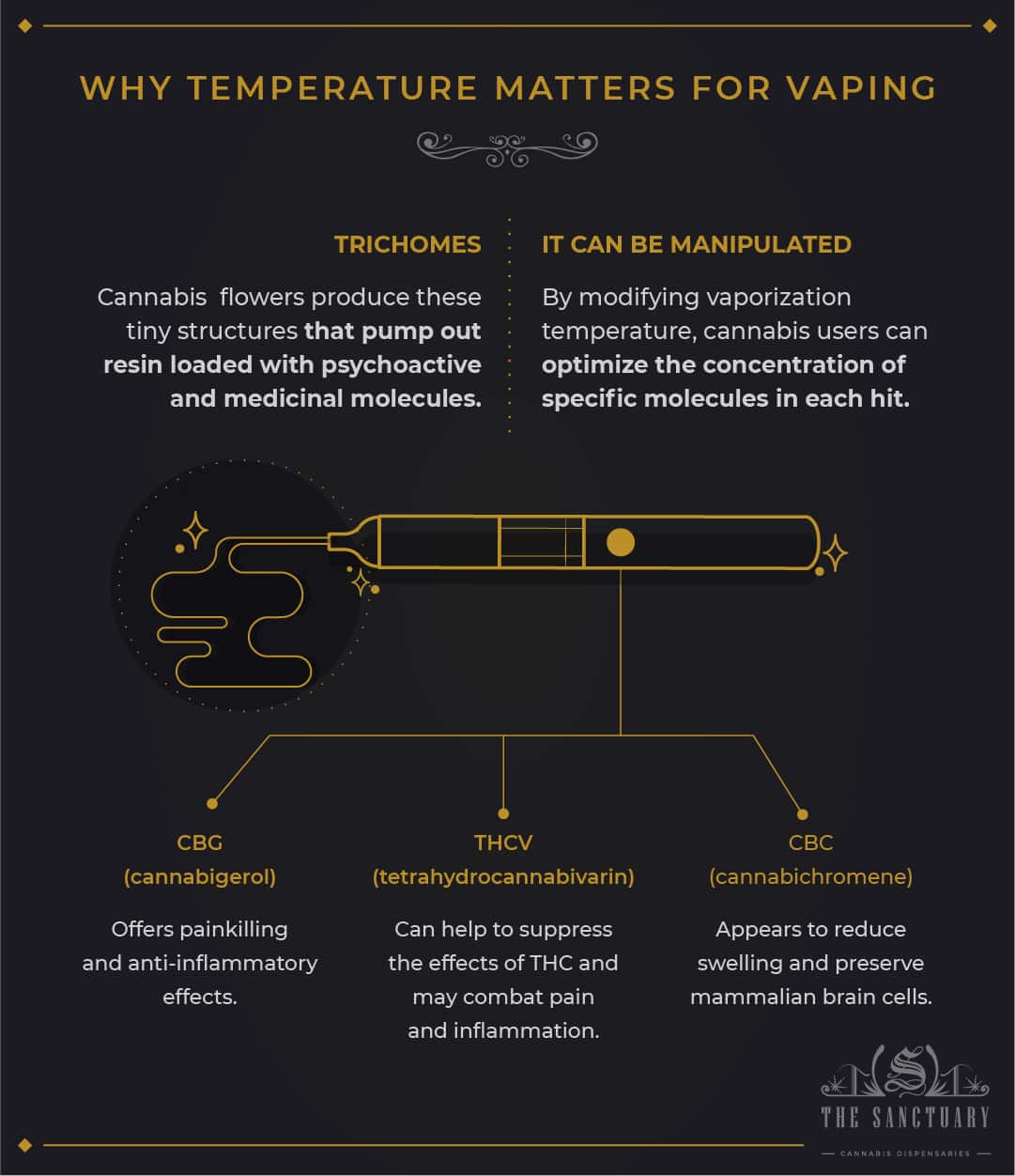
The cannabis plant is a factory for organic chemicals. It generates trichomes, which are tiny mushroom-shaped outgrowths. These microscopic structures produce resin rich in psychoactive and therapeutic compounds.
There are over 100 cannabinoids, over 100 terpenes, and several flavonoids in this collection. Cannabis users may customize the concentration of particular chemicals in each hit by adjusting the vaporization temperature.
Other major and minor cannabinoids are receiving greater attention in science. CBG (cannabigerol) has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties in studies. THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin) is a cannabinoid that can assist to inhibit the effects of THC while also combating pain and inflammation.
Cannabichromene (CBC) appears to decrease swelling in mammalian brain cells while also preserving them. As science develops, more data will inevitably emerge.
Ideal temperature ranges for cannabis
At different temperatures, cannabis users might expect varied psychotropic effects. This varies based on the person and cannabis strain. The following is a temperature guideline for the most prevalent cannabis compounds:
Low: 246–320 degrees Fahrenheit
THC can be liberated by vaping in this range of temperatures. This level also targets a variety of terpenes, which contribute to the pleasant flavor and medicinal benefits of cannabis.
- THC: 314 degrees Fahrenheit: THC is the psychoactive ingredient in cannabis. THC passes across the blood-brain barrier and activates CB1 receptors in the brain. THC causes a rapid increase in the neurotransmitter dopamine by altering the firing pattern of neurons. Euphoria, cheerfulness, and a rise in hunger ensue as a result of this. THC at high doses can create a profoundly changed state of consciousness, which might make some users anxious.
- Caryophyllene: 246 degrees Fahrenheit: In most strains of weed, caryophyllene is the most prevalent terpene. Because of its existence in foods like black peppercorn and its impact on the CB2 receptor, the molecule is also known as a dietary cannabinoid. By decreasing inflammation, caryophyllene may aid with pain management.
- beta-Sitosterol: 273 degrees Fahrenheit: One of the flavonoids present in cannabis is beta-Sitosterol. The chemical has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties.
- alpha-Pinene: 312 degrees Fahrenheit: Rosemary and pine flavors are added using alpha-Pinene. The terpene has anti-anxiety properties and may assist to mitigate THC’s negative effects, including impairment of short-term memory. Pinene and THC may work together to improve pulmonary airflow.
Low-Medium: 320–356 degrees Fahrenheit
When you vape at this temperature, you’re inviting some really intriguing compounds into the mix. This is the best range for releasing CBD alongside essential terpenes if you’re smoking high-CBD flower. If you’re vaping high-THC flower, this temperature will release a lot more terpenes.
- CBD: 356 degrees Fahrenheit: CBD has a soothing and relaxing effect, but unlike THC it is non-psychoactive. CBD, on the other hand, is thought to counteract some of THC’s effects by temporarily inhibiting CB1 receptors. CBD also is thought to work through a variety of additional biochemical mechanisms to reduce inflammation and provide antioxidant and neuroprotective benefits.
- Myrcene: 334 degrees Fahrenheit: The most prevalent terpene in cannabis is myrcene, which becomes accessible at this temperature range. Grapes, spice, and earthiness are some of the flavors provided by the molecule. Myrcene is the terpene responsible for most indica strains’ calming effects.
- Delta-8-THC: 352 degrees Fahrenheit: Delta-8-THC gives this temperature range a mild psychedelic effect. It’s a THC analog that binds to CB1 receptors and has appetite-stimulating, anti-nausea, pain-relieving, anti-anxiety, and neuroprotective properties. Delta-8-THC, on the other hand, is found in extremely tiny levels in cannabis. It also has a lesser hallucinogenic potency than its more well-known cousin.
- Cineole: 348 degrees Fahrenheit: Cineole is a terpene that has a lot of potential. It’s one of the most important components of eucalyptus, yet it’s uncommon in today’s cannabis strains. Antiviral, analgesic, antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and antifungal properties have been established for this terpene. Cineole improves cerebral blood flow as well.
- Limonene: 350 degrees Fahrenheit: Limonene imparts citrus notes to cannabis smoke. The chemical enhances THC’s cerebral and pleasurable effects. In animal studies, limonene decreased anxiety and boosted levels of serotonin and dopamine in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus.
- p-Cymene: 350 degrees Fahrenheit: Found in both thyme and cumin is p-Cymene. It has a citrusy and sweet flavor and demonstrates a sedative effect according to animal studies.
- Apigenin: 352 degrees Fahrenheit: This molecule is the main anxiolytic agent present in chamomile flowers and has anti-anxiety properties. It works on the same receptors as benzodiazepines but does not produce amnesia or drowsiness, which is impressive. Although there is significant potential for apigenin to be developed as a cancer chemopreventive drug, human clinical studies investigating its influence on disease prevention have not been undertaken.
Medium-High: 356-390 degrees Fahrenheit
The medicinal effects of cannabis vapor are enhanced by this temperature bracket. A sedative and calming effect is also added by the administration of a specific cannabinoid.
- CBN: 365 degrees Fahrenheit: The first cannabinoid isolated from cannabis was CBN (cannabinol). It is not produced by enzymatic processes in the plant, unlike other cannabinoids. CBN, on the other hand, is the consequence of THC breakdown. CBN will provide a sedative component to the high, as well as anti-inflammatory properties. CBN has also shown potential as an anticonvulsant and may help with psoriasis symptoms.
- Cannflavin A: 356 degrees Fahrenheit: Cannflavin A is a flavonoid that may be found in higher concentrations in cannabis leaves. The chemical has anti-inflammatory effects that are remarkable.
- Linalool: 388 degrees Fahrenheit: Linalool gives many weed strains a strong floral fragrance with notes of lemon and lavender. A number of cannabis’ putative medicinal effects are credited to linalool. Anti-anxiety, antidepressant, and immunopotentiation characteristics are all present in the molecule, which enhances numerous immune activities directly.
High: 390 degrees Fahrenheit and above
This is the extreme of the temperature range. More helpful terpenes and cannabinoids may be found here. Things, on the other hand, are starting to heat up. This is when vaping resembles smoking, and certain harmful chemicals are converted to gases.
This temperature range is considered to liberate all of the therapeutic components found in cannabis flower, however, it is a delicate balance between vaporization and the release of detrimental toxins.
- Benzene: 392–689 degrees Fahrenheit: While the majority of the chemicals listed above are considered helpful, benzene is not one of them. One of the reasons why many cannabis users are quitting smoking is because of this carcinogen. The carcinogenic characteristics of benzene have long been known; high amounts of benzene have been linked to an increased incidence of leukemia in individuals. Benzene has a boiling point of 176 degrees Fahrenheit, but it has been proved that some vape types can remove the molecule up to 392 degrees Fahrenheit. There is currently no verified value for the benzene vaporization point in cannabis use. According to some reports, the temperature might reach 689 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Terpineol: 424 degrees Fahrenheit: Terpineol has a light lilac fragrance and is often found in cosmetics and perfumes. The terpene has been shown to have sedative, antimalarial, antioxidant, antibacterial properties, among other things.
- THCV: 428 degrees Fahrenheit: At higher temperatures, THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin) evaporates. This cannabinoid is a derivative of THC that exists in trace amounts. There are, however, cannabinoid-rich varieties. CB1 receptors are activated and blocked by THCV. Anticonvulsant effects have been linked to cannabinoids, and they have been found to help with inflammation and pain. THCV may also help with fat metabolism and weight reduction.
- Pulegone: 435 degrees Fahrenheit: It could be worth it to heat your vaporizer to these degrees to get this terpene. The chemical has sedative and memory-enhancing properties. Pulegone may also help with fevers, according to some research.
- Quercetin: 482 degrees Fahrenheit: Quercetin is a flavonoid found in cannabis that has antioxidant properties comparable to vitamin C. The chemical also has antiviral and anticancer properties.
The content provided on this blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical, legal, or professional advice. Cannabis use is subject to local laws and regulations, which vary widely by jurisdiction. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or altering an existing treatment regimen. The authors and publishers of this blog are not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided herein. Use cannabis responsibly and in accordance with applicable laws. This blog is intended for adults aged 21 and over. The Sanctuary Dispensaries D186, D187.








