Iftikhar Alam
Author
Reviewed by Cannabis Experts
Published on: May 6, 2021 | Updated on: July 28, 2024
Both CBD and kratom are being studied for their potential to treat issues including chronic pain, anxiety, and drug addiction.
Some individuals believe kratom might be a good CBD replacement. They may appear to share some similar ground on the surface. The two compounds, however, have significant distinctions. On a molecular level, these two herbal medicines function in distinct ways and have different dangers and adverse effects.
What is kratom?
Kratom is a tree native to Southeast Asia that goes by the name “mitragyna speciosa.” Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea are among the nations where it grows natively. For thousands of years, people in these places have utilized kratom. The leaves are eaten traditionally by locals for their stimulant-like effects.
At low dosages, kratom works as a stimulant, similar to coffee. Its effectiveness as an energy booster and dietary supplement is due to these properties. Kratom, on the other hand, has properties that are comparable to opiates at large dosages.
Kratom is the world’s sole natural supply of opioid alkaloids, aside from the poppy plant and akuamma seeds. For this reason, kratom has a long history of usage as an opiate replacement.
Though the plant contains more than 40 distinct alkaloids, two of them, mitragynine (MG) and 7hydroxymitragynine (7HMG), have recently come under examination. MG appears to be medicinal, similar to how CBD and THC interact, whereas 7-HMG exhibits psychoactive effects. While MG is the most prevalent component in kratom, 7-HMG binds to the same brain receptors as opioids, putting kratom’s legality in jeopardy.
Kratom may be eaten, smoked, or steeped in tea in its natural state. Kratom is most often crushed into a powder and combined with a liquid, most commonly warm water. Kratom, unlike cannabis, does not require heating to activate. As a result, it may be eaten uncooked, including in capsule form.
Uses for kratom
Kratom has a lengthy history of use as a treatment for a variety of ailments and symptoms. It has previously been used to address issues such as:
- Muscle pain
- Fever
- Coughing
- Hypertension
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
Despite being prohibited in some countries, it is widely eaten throughout Southeast Asia at social events. In today’s world, it’s widely used to treat:
- Anxiety
- Chronic pain
- Energy booster
- Opiate withdrawal
Kratom, unlike cannabis, does not offer instant relief. In most cases, the effects of kratom are felt within an hour.
One of the most popular applications for kratom is pain treatment. Over 90 percent of participants in an online poll done by the Pain News Network in cooperation with the American Kratom Association considered kratom to be extremely helpful for pain management.
Kratom has long been used to treat withdrawal from drugs, particularly opioids. The opioid problem in North America is partly the reason for the surge in popularity of kratom. Many users have discovered that kratom is quite successful in weaning them off of stronger opioids like fentanyl, heroin, and oxycodone.
Some people have been able to use kratom to completely eliminate the symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
People have also claim to have had success using kratom in treating anxiety problems. Kratom has been used to treat conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and social anxiety disorder (SAD). It can also have an anti-inflammatory impact on the body.
This might make it a viable therapy option for joint and bone discomfort. More clinical studies are needed, however, before kratom can be completely endorsed as a therapy for these diseases.
What is CBD?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the second most common active component in cannabis. CBD is extracted directly from the hemp plant, which is a relative of the cannabis plant and is an important component of medicinal cannabis.
While CBD is a component of cannabis, it does not produce a “high” on its own. For legal reasons, the majority of CBD on the market is produced from hemp. It’s usually extracted as an oil, which is then processed and marketed as capsules, CBD-infused foods, and tinctures, among other things. There are a variety of extraction techniques available, ranging from CO2 extraction to solvents such as ethanol or butane.
Full-spectrum CBD products may contain other cannabinoids and terpenes that were extracted along with it because it is made from the complete plant. While CBD is useful on its own, many people find that it works better when combined with other cannabinoids, such as THC. By federal law, full-spectrum CBD oil products can include up to 0.3 percent THC.
CBD isolate, on the other hand, is a CBD product that contains only CBD and no additional cannabinoids or terpenes. Many consumers choose isolate goods over full-spectrum ones because they are concerned about testing positive for THC. Full-spectrum and isolate CBD may be available as vape liquids, gummies, capsules, and tinctures, among other items.
CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) to perform its activities. In the human body, the ECS is a natural, endogenous network of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors. ECS receptors are found in virtually all cell types, which explains CBD’s wide variety of applications.
Uses for CBD
One of CBD’s most well-known properties is its ability to alleviate various forms of pain. Its applications, however, are not limited to pain relief. It was recently revealed to have potent anti-inflammatory properties. CBD has been shown to be a helpful therapy for a variety of ailments, including:
- Headaches and migraines
- Arthritis
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Neuropathic pain from multiple sclerosis
CBD has proved to be an effective anti-anxiety treatment. Numerous animal and human research have shown that treating anxiety and stress illnesses such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and social anxiety disorder might be beneficial. CBD has even been found to help with other illnesses that are exacerbated by anxiety.
Some individuals have experienced a reduction in insomniac symptoms after using CBD to alleviate their anxiety. Individuals suffering from drug withdrawal have also found CBD to be beneficial. CBD may not only help with withdrawal symptoms like depression and anxiety, but it may also help with cravings and relapses, according to research.
What is the difference between kratom and CBD?
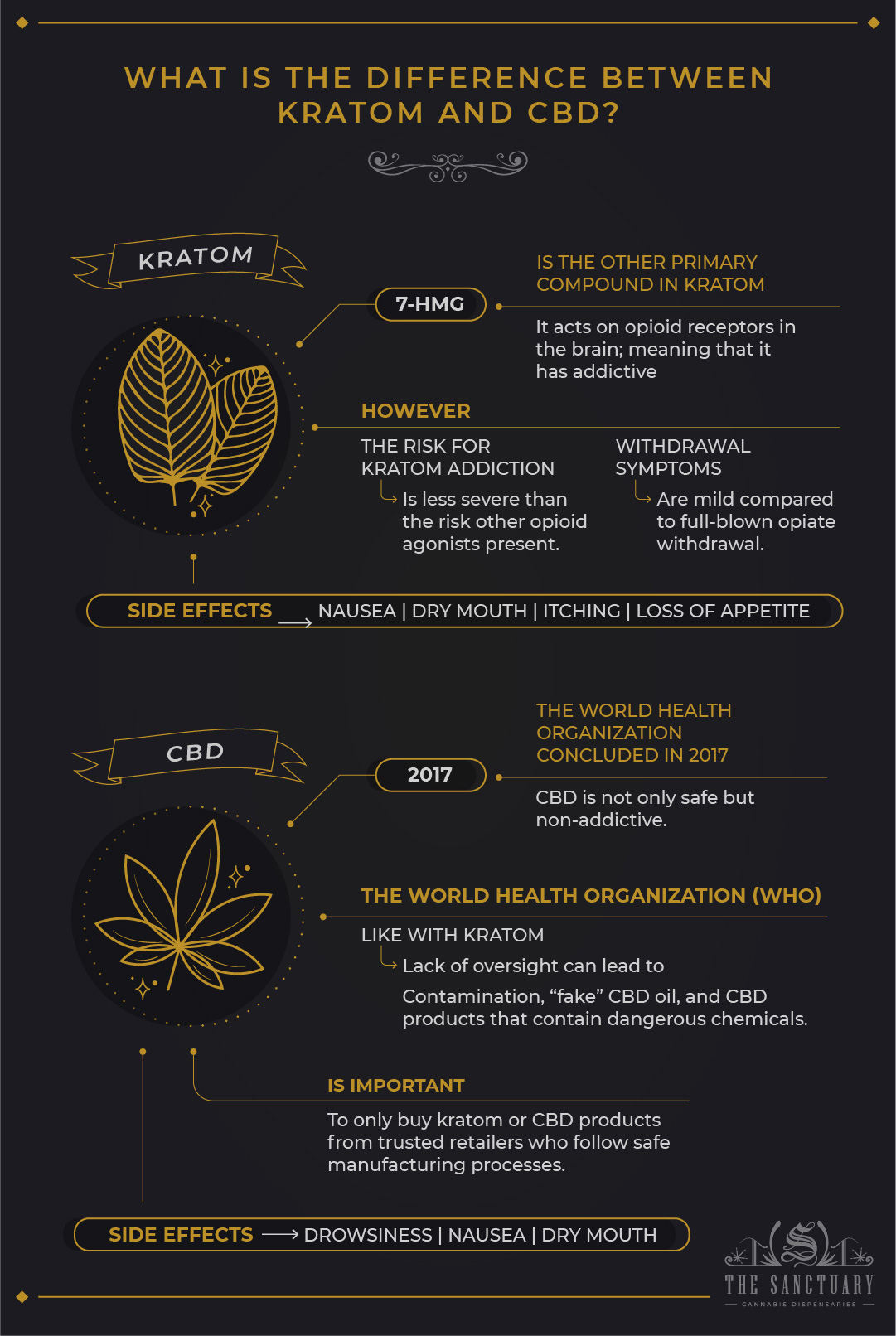
While mitragynine (MG) may be able to cure opioid addiction, the second major component in kratom, 7HMG, activates opioid receptors in the brain, which means it has the potential to be addictive, which is why the FDA is concerned.
After taking kratom frequently for more than 6 months, virtually all of the participants showed indications of addiction, according to a 2014 poll consisting of 293 persons. Pain, sleeping difficulties, and rage were among the physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms reported. It’s worth noting that the danger of kratom addiction is lower than the risk of other opioid agonists.
Furthermore, as compared to full-blown opiate withdrawal, the withdrawal symptoms of a kratom addiction are moderate. However, kratom’s addiction risk is a disadvantage when compared to CBD, which has no danger or risk of side effects.
Kratom has the potential to be addictive, however, it can also have negative side effects such as:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Itching
Kratom has been linked to 44 deaths, according to the FDA. Many supporters feel this is fearmongering, as kratom was almost always taken in conjunction with other medications in these situations. However, it does not rule out the potential that kratom is harmful, particularly when combined with other substances such as over-the-counter and prescription medicines.
In early 2018, a salmonella epidemic connected to kratom products infected 199 individuals in 41 states, further damaging the plant’s image. As a result, the FDA examined kratom products from several brands and discovered salmonella in a high percentage of them, resulting in multiple recalls.
CBD looks to be relatively safe, with just a few minor adverse effects being recorded, such as:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Drowsiness
In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) published a report claiming that CBD is both safe and non-addictive. However, like with kratom, a lack of regulation may lead to concerns like contamination, “fake” CBD oil, and CBD products containing hazardous compounds.
These problems emphasize the significance of purchasing kratom or CBD products exclusively from reputable vendors that use safe production methods.
Is kratom and CBD legal?
Kratom’s legal status varies from nation to country and state to state. It has been designated as a restricted drug in countries such as Poland, Germany, and New Zealand. Other countries, like Australia, Myanmar, and Thailand, have declared it illegal outright.
Always double-check the legal status of kratom in your nation, region, and city, as it varies by jurisdiction.
The legal status of kratom in the United States is always in jeopardy. Its strong ties to painkillers have drawn the ire of US politicians. The US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) attempted to outlaw kratom for the first time in 2016.
The US Food and Substance Administration (FDA) proposed that kratom be classified as a Schedule I drug, similar to other opioid drugs, in 2017. Following a public uproar, the DEA and FDA decided not to act on these suggestions, which means that kratom remains legal on the federal level.
Several states have taken the initiative to outlaw kratom on a state-by-state basis. Several states, including Alabama, Indiana, and Tennessee, have made kratom illegal. Denver, San Diego, and Sarasota, among other American cities, have chosen to make kratom illegal in their jurisdictions.
Although hemp is not categorized the same as cannabis, the wording of federal cannabis legislation sometimes provides space for interpretation. In the end, hemp-derived CBD products are lawful, however, state laws may differ. CBD is only available at dispensaries in select states, such as Ohio.
The content provided on this blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical, legal, or professional advice. Cannabis use is subject to local laws and regulations, which vary widely by jurisdiction. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or altering an existing treatment regimen. The authors and publishers of this blog are not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided herein. Use cannabis responsibly and in accordance with applicable laws. This blog is intended for adults aged 21 and over. The Sanctuary Dispensaries D186, D187.








