Iftikhar Alam
Author
Reviewed by Cannabis Experts
Published on: November 24, 2021 | Updated on: September 10, 2024
While smoking cannabis flower is still the most common way of consumption, more people are opting to smoke, dab or vape high-potency concentrates for a fresh and unique experience.
There are numerous types of cannabis extracts to select from, including shatter, isolate, live resin, rosin, budder, sugar, and so on.
Due to their similar names and relatively similar shapes, the distinctions between live resin and rosin are often misunderstood, however, there are some significant variances between these two extracts.
What does “live” mean?
“Live” may be a perplexing phrase for cannabis users who are new to concentrates or for lovers of concentrates who want to extend their understanding. Does this imply that there are still live cells in the concentrate, like with probiotics?
The word “live” refers to concentrations that have been derived from freshly harvested plant materials when it comes to concentrates. The most popular forms of concentrates (shatter and wax, for example) are taken from plant material that has been dried and cured before processing. The most frequent process for preparing bud for sale is drying and curing it, which is usually required to produce a high-quality product.
Live concentrates, unlike other types of concentrates, are not dried or cured before being processed. After the bud has been cut, it is dried for a week or two. This traps terpenes while removing a lot of moisture.
After that, the bud is cured for another 2-8 weeks before being distributed and sold. A properly dried and cured bud will have a low moisture content, preserving it while also allowing it to burn smoothly. Because the chlorophyll is broken down during the curing process, it will have a rich, fragrant flavor. (Due to the extra chlorophyll, improperly cured bud is harsher, weaker, and smells like hay.)
While this prepares the bud for sale, the drying and curing process removes moisture from the flowers, which causes the buds to lose some of their terpenes. Most customers do not notice anything lacking since the bud or concentrate produced from it is still tasty and powerful.
All of the plant’s terpenes are maintained in the finished product when extracting concentrate from fresh plant materials using “live” extraction. As a result, a high-quality concentrate is produced that is considerably more delicious and, due to the entourage effect, potentially stronger.
What is live resin?
Before getting into the specifics of live resin and rosin, it is important to note that they are both classified as cannabis concentrates or extracts, depending on who you ask. Even though they are generated from the same parent material, live resin and rosin have significant variances, thus putting them on different extremes of the cannabis concentrate spectrum.
Beyond our senses of sight and smell, live resin is distinguished by its golden hue and granular form. It is, first and foremost, a step up from the rest of the solvent-based concentrates on the market. When utilizing hydrocarbon processing, one of the greatest reasons to extract using fresh frozen flower is the presence of live resin.
Many other popular concentrates on the market that employ dried, cured cannabis instead of fresh cannabis lose natural terpenes throughout the production and extraction process.
Live resin can give consumers a product that keeps much more of its natural terpene profile thanks to the use of fresh frozen flower.
When comparing live resin vs. non-live hydrocarbon alternatives, it is generally considered above any other solvent-based extracts that employ dried-and-cured source material. Live resin’s naturally preserved terpenes make it more pleasurable to consume than other solvent-based products, which are frequently manufactured with a lower-quality source material or combined with non-single source terpenes or distillate.
Many proponents think that the best method to enjoy a cultivar’s actual benefits is to use live resin, which helps offer more of the natural full-plant sensation. The potency of the live resin full-plant experience is a major selling feature.
Live resin, like other weed extractions, has a much higher potency level than flower. The THC content of live resin can range from 65-95 percent, depending on the source material and manufacturing technique.
What is rosin?
Rosin is a cannabis extract that may be made from flower, kief, or hash. Unlike solvent-based methods that employ toxic solvents such as ethanol, CO2, or butane, rosin may be produced at home with a hair straightener or in a business environment with an industrial live rosin press that uses just heat and pressure to separate the required components.
What is live rosin?
Live rosin is manufactured in the same way as rosin, with one major difference: instead of dried and cured buds, processors utilize fresh frozen buds. Cryogenically freezing the weed immediately after harvesting maintains the plant’s inherent components, resulting in a greater cannabinoid and terpene output.
That implies a stronger high and greater flavor for you. The drying and curing procedure for rosin is designed to minimize the amount of moisture and chlorophyll in the dried bud before ingestion.
However, the plant’s readily evaporated terpenes are lost during the drying process, resulting in diminished flavor and effects. Live rosin preserves the plant’s natural entourage effect by retaining minor components.
Differences in making live resin vs. rosin
Those who want to make their own concentrates for business or personal use should think about the methods involved. Live resin would almost certainly have beginning expenses in the six figures, whereas rosin will most likely be in the mid-five figure range for a commercial lab and much less for a home hobbyist.
The increase in live resin prices is due to the solvents used in the process as well as the safety considerations that come with certification. Additional safety precautions include anything from more advanced fire extinguisher and exhaust systems to the construction of full-scale blast-safe chambers to prevent any explosions or fires (known as C1D1 rooms).
Due to the natural ingredients, however, the manufacturing of rosin is a lot simpler procedure. The transition from hair straighteners to dedicated machines greatly improved the uniformity of solventless products, resulting in what many refer to as the “rosin revolution” that we are currently witnessing.
How to make live resin
The processes of making live resin and other solvent-based cannabis concentrates should only be done by professionals, as they can be extremely dangerous.
Live resin is extracted using the same methods and chemicals as other concentrations. It is commonly referred to as butane hash oil (BHO), although it is done using live or flash-frozen plants, with CO2 extraction as an option.
If the cannabis is going to be used for live resin, producers usually flash-freeze it right after harvest and keep it chilled throughout the extraction process to keep the active components safe. Liquid nitrogen or dry ice can be used to chill the plant material.
How to make rosin
Cannabis flower, hash, or kief can all be used to make rosin. These raw ingredients are simple to convert into rosin wax. Rosin is hard to differentiate from shatter or wax in terms of appearance.
The distinction between the two is that rosin is totally devoid of the residual solvents that hydrocarbon extraction procedures frequently leave behind (e.g. butane, propane, etc.). You can make your own concentrate at home without the risks that come with solvents.
Items needed
You will need a few things to get started. Most of these goods are likely already in your house, but if not, you should be able to get them quickly and affordably.
- Hair straightener (look for one with a low-temperature setting of approximately 300 degrees Fahrenheit or less—any higher and important terpenes will evaporate)
- Cannabis (this can be flower, kief, or bubble hash)
- Parchment paper (unbleached, if possible)
- Metal tool (dabber tools)
- Concentrate dish (silicone works well)
Step by step process
- Set your hair straightener to the lowest setting possible (280-330 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Cut a small piece of parchment paper for your weed material.
- Half-fold the parchment paper.
- Between the folded parchment paper, place your material.
- With your fingertips, lightly press the folded parchment paper.
- With your hair straightener, carefully line the buds within the paper together and apply strong pressure for 3-7 seconds. Before releasing the pressure, look for any traces of secretion from the material, which indicates that resin has been released.
- Remove the paper and cannabis from the hair straightener.
- Unfold the parchment paper and remove the pressed material with your dabber tool. Use different clean sheets of parchment if you plan on doing multiple presses with new material.
- Scrape off the resin and collect it into a concentrate dish.
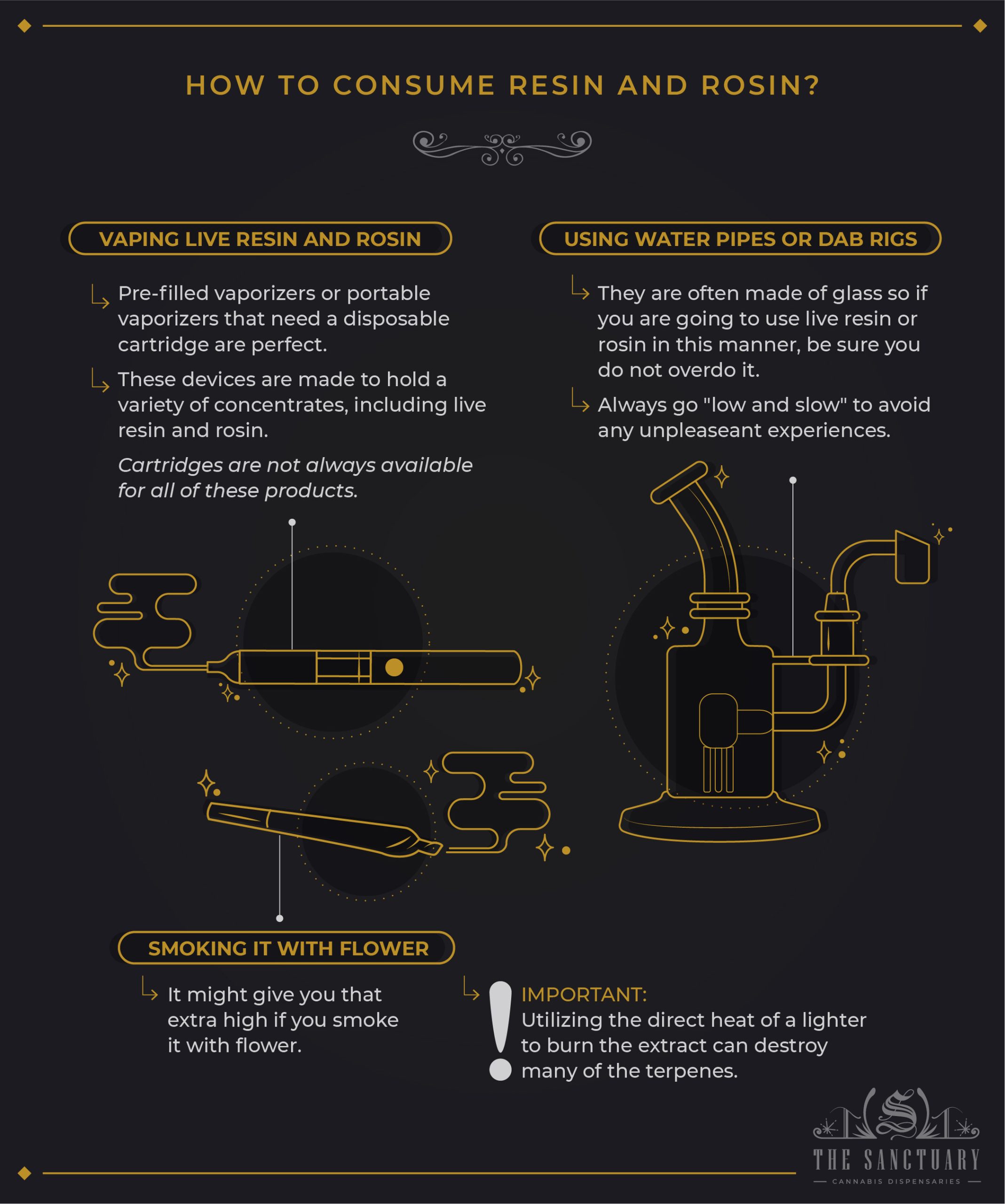
How to consume resin and rosin?
Handheld vaporizers or water pipes are often used to ingest live resin and rosin. Smoking, vaping, and dabbing rosin and resin are all options.
Vaping live resin and rosin
For cannabis users who prefer a simple, discrete way of usage, pre-filled vaporizers or portable vaporizers that need a disposable cartridge are perfect. These devices are made to hold a variety of concentrates, including live resin and rosin.
You may sample a range of cannabis products in disposable cartridges if you buy your own mobile vape. Cartridges are not always available for all of these products.
Using water pipes or dab rigs
Water pipes designed for concentrate usage are known as dab rigs, and they are often made of glass. If you are going to use live resin or rosin in this manner, be sure you do not overdo it.
To avoid an unpleasant experience while using live resin or rosin, always go “low and slow.” Dab rigs are available at your neighborhood head shop or dispensary.
Smoking it with flower
When combined with your preferred strain of flower, smoking live resin or rosin might give you that extra high you have been waiting for. Unfortunately, utilizing the strong and direct heat of a lighter to burn the extract can destroy many of the fragrant and delicious terpenes.
Sources
Footnotes
- Lamy FR, Daniulaityte R, Zatreh M, Nahhas RW, Sheth A, Martins SS, Boyer EW, Carlson RG. “You got to love rosin: Solventless dabs, pure, clean, natural medicine.” Exploring Twitter data on emerging trends in Rosin Tech marijuana concentrates. Drug and alcohol dependence. 2018;183:248-52.
- Meehan-Atrash J, Strongin RM. Pine rosin identified as a toxic cannabis extract adulterant. Forensic science international. 2020;312:110301.
- Lindholst C. Long term stability of cannabis resin and cannabis extracts. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences. 2010;42(3):181-90.
- Trofin IG, Dabija G, Vaireanu DI, Filipescu LA. The influence of long-term storage conditions on the stability of cannabinoids derived from cannabis resin. Rev Chim Bucharest. 2012;63(4):422-7.
References
- Live Rosin vs Live Resin: What is the Difference?. Precision Extraction Office. Accessed 4/9/2024.
- Live Rosin vs Live Resin. Lowtemp Industries. Accessed 4/9/2024.
- Live Resin vs Rosin: Which Is Right for You?. NuggMD. Accessed 4/9/2024.
The content provided on this blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical, legal, or professional advice. Cannabis use is subject to local laws and regulations, which vary widely by jurisdiction. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or altering an existing treatment regimen. The authors and publishers of this blog are not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided herein. Use cannabis responsibly and in accordance with applicable laws. This blog is intended for adults aged 21 and over. The Sanctuary Dispensaries D186, D187.